Vehicular Geo-Obfuscation
The goal of this project is to protect vehicle location privacy in various location based applications.
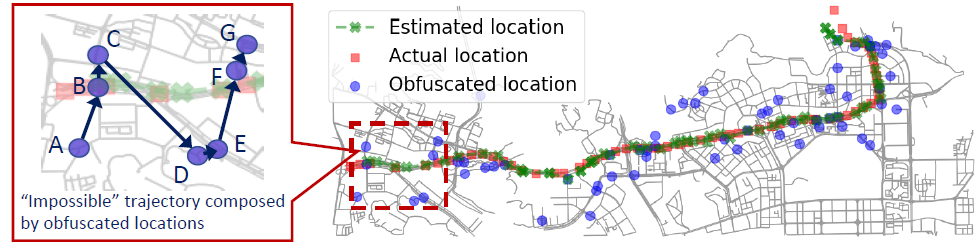
Task 1: Traffic flow aware inference attacks. Thinking like an adversary, we propose a new threat model that leverages traffic flow information to recover vehicles’ exact locations from other types of information, such as braking signals or perturbated locations. We describe the target vehicle’s mobility by a hidden Markov model (HMM) (Figure 1), and then track the vehicle’s exact locations using the Viterbi algorithm (Figure 2).

Publications: Sigspatial 2022, IPSN 2020
The MATLAB code of vehicle location tracking has been released here.
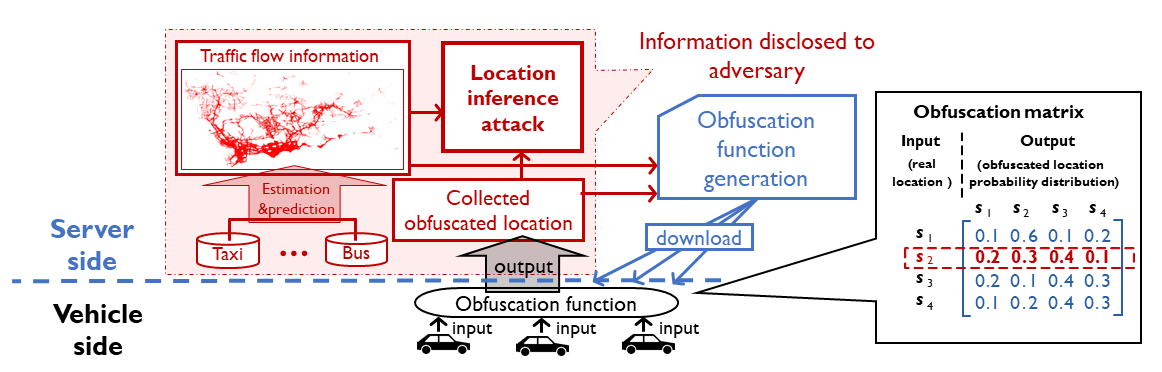
Task 2: Location obfuscation over the road networks. Considering that individual vehicles’ mobility is restricted by various road environments, including traffic flows and local road network topology, our objective is to design time-efficient obfuscation techniques to protect vehicles’ location privacy against the traffic-aware inference attacks.
Publications: TMC 2020, CIKM 2020, ICDCS 2019
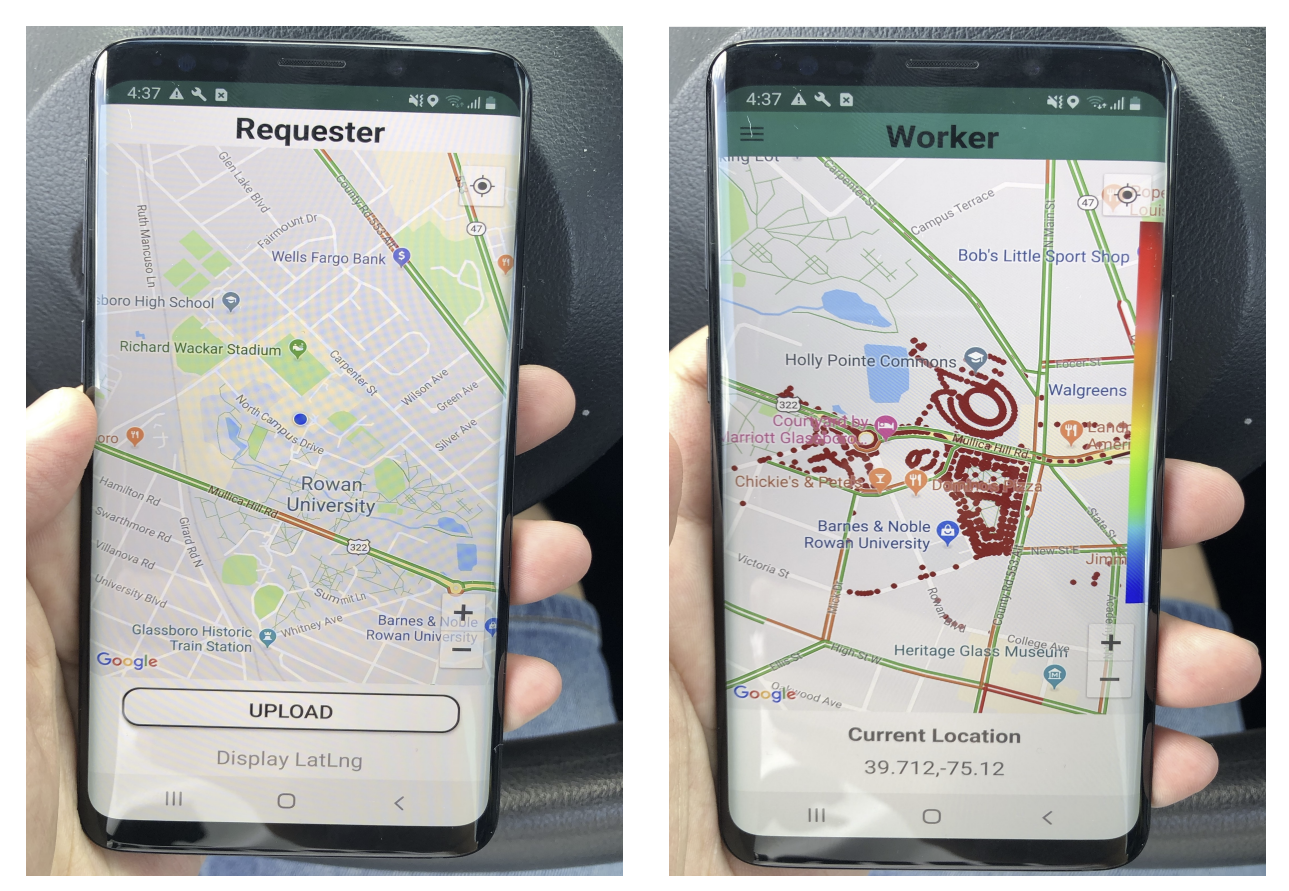
Task 3: Vehicle Spatial Crowdsourcing (SC) Platform. We have built a prototype of SC, which encompasses essential features such as task request/assignment and geo-obfuscation. To enhance user accessibility, we’ve created an Android application utilizing the Google Maps API, as depicted in Figure 4. The application enables users to register/log in as either a requester or a worker. Requesters can conveniently upload tasks with specified locations, while workers can download a Geo-Obfuscation (GO) matrix from the server. Using this matrix, a worker can choose an obfuscated location and potentially receive a task assignment from the server. Upon receiving a task, the worker has the option to accept it by clicking the “accept” button, triggering the display of a navigational route on the map guiding them to the task location.
Publications: NA