SpatialAgent - SC Platform
A Spatial Crowdsourcing (SC) platform to efficiently assign spatial tasks to crowdsourced workers.
Overview
In an increasingly interconnected world, the need for efficient and privacy-centric emergency response systems has become paramount. “SpatialAgent” aims to address this challenge by proposing a novel spatial crowdsourcing platform that incorporates cutting-edge privacy protection technologies to safeguard user privacy while providing timely assistance to those in need. By leveraging privacy-enhancing technologies like Differential Privacy, the system aims to create a seamless and secure platform for emergency help requests and response coordination.
Major Goals of SpatiaAgent
- The project’s foremost goal is to implement robust privacy protection measures for both patients and responders. By utilizing data perturbation techniques and the LIH algorithm, the system ensures that responders’ locations remain confidential, mitigating potential risks associated with sharing sensitive information.
- Indoor Navigation The second objective of the project is to facilitate seamless indoor navigation for responders. By preparing a directed graph of building layouts, the system can generate optimal paths, enabling responders to navigate complex indoor environments and locate patients effectively.
Architecture
The architecture is divided into implementations - each serving distinct roles to ensure the privacy of users and offer seamless navigation for responders.
Frontend Implementation: User Interface and User Experience
- The Frontend Implementation of the proposed architecture centers around developing intuitive User Interfaces (UI) to facilitate user interactions. Two key interfaces have been designed: the Patient Interface and the Responders Interface. The Patient Interface empowers users to register help requests, utilizing operational and mapping APIs from the backend to provide accurate and real-time location information. Additionally, the app integrates obfuscation functionality to further protect user data, leveraging a suite of APIs for enhanced privacy.
Backend Implementation: Mapping APIs, Obfuscation APIs, and Operational APIs
- The Backend Implementation plays a pivotal role in enabling the architecture’s functionality. It leverages various APIs, including Google Maps API for map-based navigation and operational APIs for handling user requests and responder information. To protect responder locations, an innovative Obfuscation API is integrated, employing the Location-based Information Hiding (LIH) algorithm, implemented using MATLAB, to generate obfuscated locations for responders without compromising their privacy.
Python Flask and MongoDB: Backend Support and Database
- Supporting the backend functionalities, the project utilizes Python Flask, a lightweight web framework, to handle API requests and perform computations efficiently. MongoDB, a NoSQL database, has been chosen due to its compatibility with both React Native (frontend framework) and Python Flask (backend framework). It stores crucial information about patient requests and responder details securely, allowing for seamless retrieval and manipulation of data.
Architecture Layers: Client Layer, Server Layer, and Database Layers
- The proposed architecture is designed around a layered structure to ensure modularity and scalability. At the core lies the Client Layer, consisting of two user interfaces - the Patient Interface for help requests and the Responders Interface for volunteer response. The Server Layer, in conjunction with the Backend APIs, handles the computation and processing of user requests, responses, and navigation details. Finally, the Database Layer securely stores essential information related to patient requests and responder profiles.
- With an emphasis on indoor navigation, the project prepares a directed graph based on building layouts, allowing for guided path generation to aid responders in reaching patients promptly. Google Maps API facilitates real-time location sharing, enabling accurate path planning and navigation for responders.
Privacy Protection through Obfuscation APIs and LIH Algorithm
- To safeguard responder privacy, the architecture employs Obfuscation APIs, which integrate the LIH algorithm. This algorithm obfuscates responder locations, providing an additional layer of security against potential attackers. The obfuscated locations are dynamically computed based on the responder’s serving location, further enhancing privacy and safety.
- The LIH (Location-based Information Hiding) model’s implementation yields a probabilistic distribution table, derived from shared destination locations among responders. This table depicts the likelihood of selecting a specific site as an obscured or cloaked location within the designated region. The resultant obfuscated location serves as a strategically concealed substitute, preserving user privacy, while concurrently enabling the seamless execution of location-dependent tasks and services.
User Manual
The purpose of this manual is to guide users through the functionality and operation of the SpatialAgent - Privacy-Centric Emergency Response System app. It provides comprehensive instructions and explanations to ensure a seamless experience while using the application.
Overview. The SpatialAgent or Privacy-Centric Emergency Response System app offers two user modules - Patient and Responder. The Patient module allows users to request help during emergencies, while the Responder module enables volunteers to respond to those requests. The app employs advanced technologies to safeguard user privacy and provides responders with guided paths to reach patients swiftly.
1. Homepage and Module Section

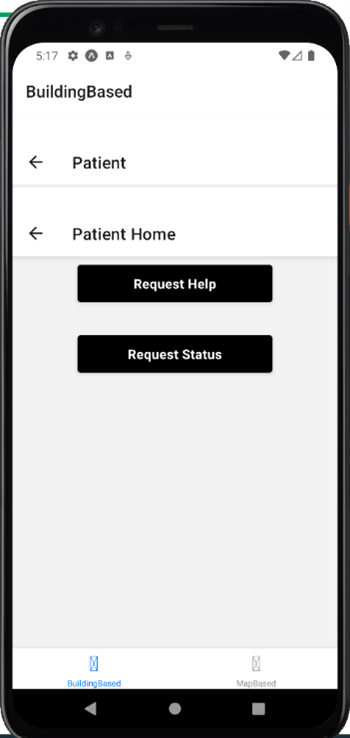
2. Patient Module
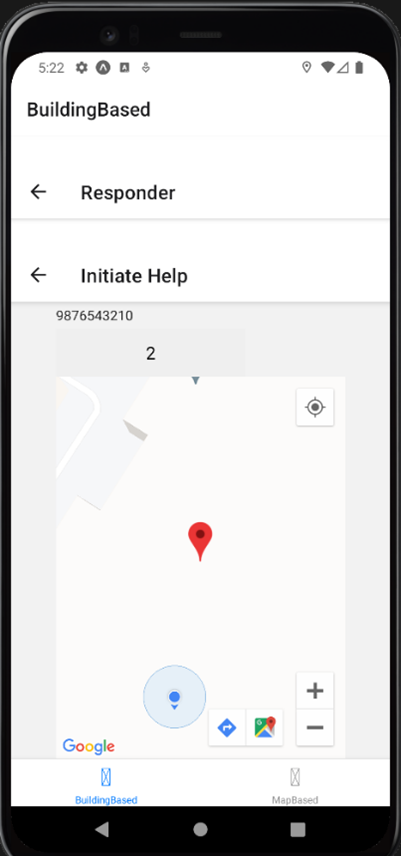
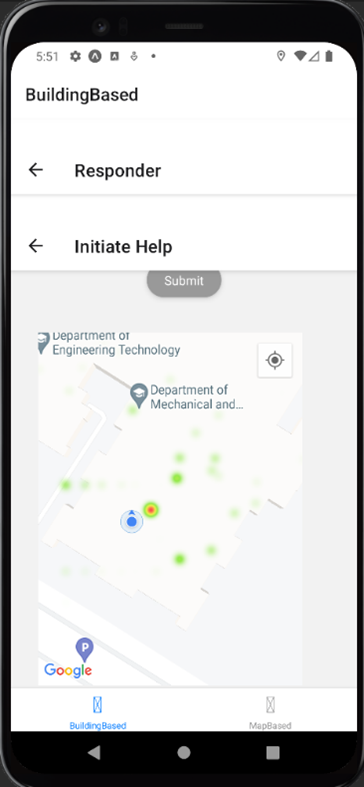
3. Responder Module

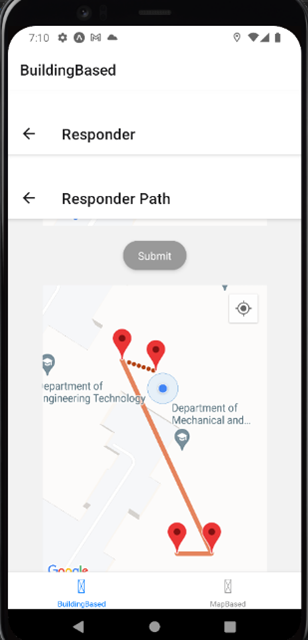
- Heat Map Visualization.
Conclusion
This project presents a comprehensive and privacy-conscious emergency response system, leveraging innovative technologies such as React Native, Python Flask, MATLAB, Google Maps API, and MongoDB. The proposed architecture ensures user privacy while providing effective assistance to those in need. In the following sections, we will delve deeper into each component and highlight their individual contributions to the project’s success.